How to Measure an Extension Spring
1. Measure the spring wire diameter, preferably to 3 decimal places for accuracy using calipers.

2. Measure the outside diameter of the coils (this may vary slightly coil to coil). Take the average value at the central coils of the body.

3. Measure the body length of the spring. The body length of the spring is the portion which excludes the hooks of looped ends. If the body is open wound, then also count the number of coils.
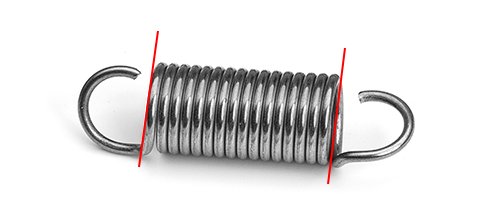
4. Measure the free length of the extension spring by measuring to the inside edge of end to end of each hook or looped end.

5. Measure the loop or hook length.
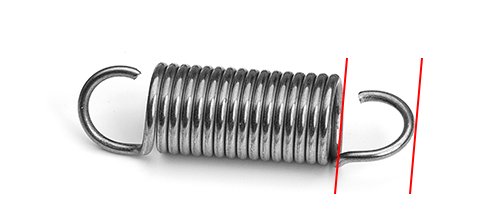
6. If the outside diameter of the loop or hook is enlarged or reduced, measure the loop or hook outside diameter.
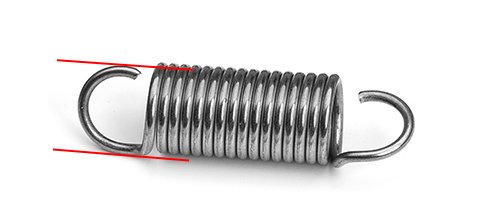
7. If the gap is important for assembly, measure the loop or hook opening. It is the distance from the end of the wire to the spring body.

8. Note the relative position of the loops or hooks if the assembly requires alignment fit. Typical specification
include:
90 degree position where the loops are twisted from each other.
In-line position where the loops are aligned in the same plane. If it is an in-line position,
then note if the assembly
specifically needs the loop openings on the same or opposite sides.
Random Position where the assembly does not matter if in-line, 90 degree, or any position in
between.

90 Degrees

Inline

Openings on the Same Side

Opening on the Opposite Side
9. Note the winding direction of the coils. In most applications this is not important but review surrounding parts and whether they require the spring to be in a specific direction.

10. Determine the spring wire material type. If the wire is not attracted to a magnet, then it might be a special metal alloy that needs exact identification. If the material is unknown, then take note of any extreme operating conditions such as: very high or low temperatures, presence of corrosive materials or rapid cycling. Learn more about Materials, and Spring Coatings and Surface Treatments.





 Sign Up/Log In
Sign Up/Log In